
Millions of people every day tap their phone on a card reader and pay at a store without pulling out their wallet. This small touch is made possible by NFC (Near Field Communication). In short, it’s a way for your device to wirelessly communicate with a nearby device, using just a tap.
You don’t need to plug anything in or pair devices like Bluetooth. For billions of ordinary users, NFC is like magic. But, it’s based on sound science and technology.
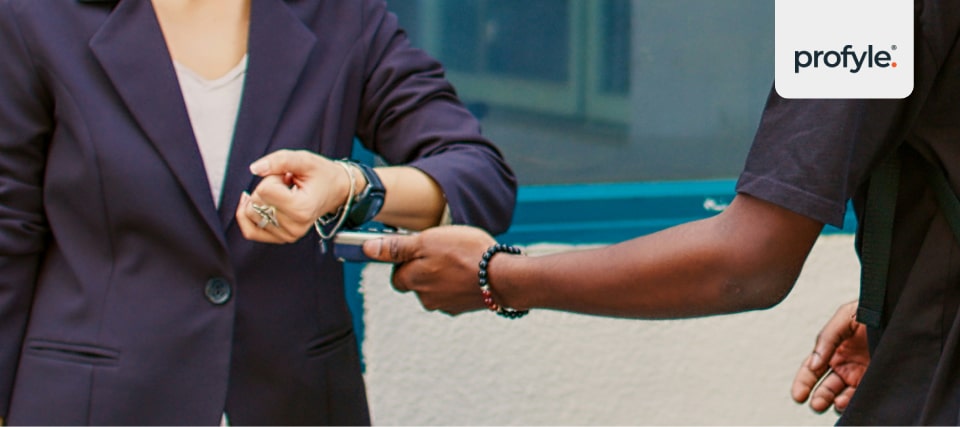

NFC technology is everywhere now, even if we don’t always notice it. We use this advanced tech almost daily. It powers everything from public transport to mobile payments. The best part? It’s reasonably secure, while being fast and convenient. Because of that, NFC is becoming a part of how we do business and interact with the world around us.
NFC technology didn’t pop out of nowhere. Its roots date back to the early 1980s when Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology was first introduced. The ability to communicate wirelessly using radio waves eventually evolved into what we now call NFC. It was established as an official standard in 2003. But, it wasn’t until smartphones, like the iPhone and Android devices, adopted the technology that it became widespread.
NFC history at a glance:
In 2020, more than 2 billion NFC-enabled devices were in use worldwide, and this number is rapidly growing. It’s estimated that by 2024, the NFC market alone will reach over $30 billion in value. This shows just how important NFC is becoming in everyday life.
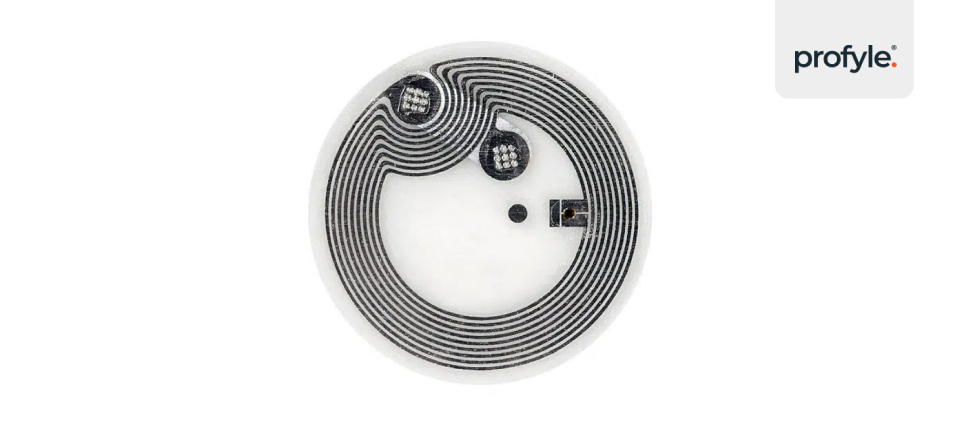

An NFC tag is a tiny, passive chip that stores information. Think of it as a smart sticker. These tags can be placed on almost anything — from product packaging to posters, wristbands, or business cards. When a phone or other NFC-enabled device nears the tag, it “reads” the stored info. This could be a website link, contact info, or a command to launch an app.

For example, Profyle uses these NFC tags on digital business cards. These cards store your professional details. A recipient can access them with a phone tap. No typing URLs, no fumbling with contacts. Just a quick, smooth info exchange.
Best of all, you can brand and design the business card to make it look appealing and fit your business. Try it for free.
The process of how an NFC tag works may sound complicated, but it’s actually quite simple once you break it down. Let’s go step by step to understand how this tiny piece of technology communicates with your phone.
One of the greatest strengths of NFC tags is their simplicity. They don’t require any fancy setup or connections, and there’s no need for an internet connection, Wi-Fi, or mobile data to make them work. NFC tags are very convenient. They are ideal for fast, secure tasks, like sharing business details, launching web pages, or making quick transactions.
NFC tags use a mix of electromagnetic fields and short-range communication to quickly and securely transfer data. This tech is perfect for payments, sharing digital business cards, or activating commands on your phone. The tags make exchanging information faster and easier than ever.
NFC tags are quietly making our lives more convenient, even if we don’t always notice them. These small, passive chips are used in various ways, making everyday tasks faster and more efficient. Here’s a closer look at some of the most common ways you can use an NFC tag today:
When you use Apple Pay, Google Pay, or Samsung Pay, NFC tags are at the core of the technology that makes it possible. With a tap of your phone at a payment terminal, your phone uses NFC to communicate securely with the terminal to complete the payment. This method is becoming more popular every year. In 2020 alone, the global mobile payment market reached $1.5 trillion, and a large portion of that was driven by NFC-enabled payments.

Many cities use NFC technology for their public transport. For example, in London, the Oyster card system has used NFC technology since 2003. Commuters just tap their card or phone to pay for rides on the Tube, buses, or trams. It saves them from fumbling with cash or tickets.
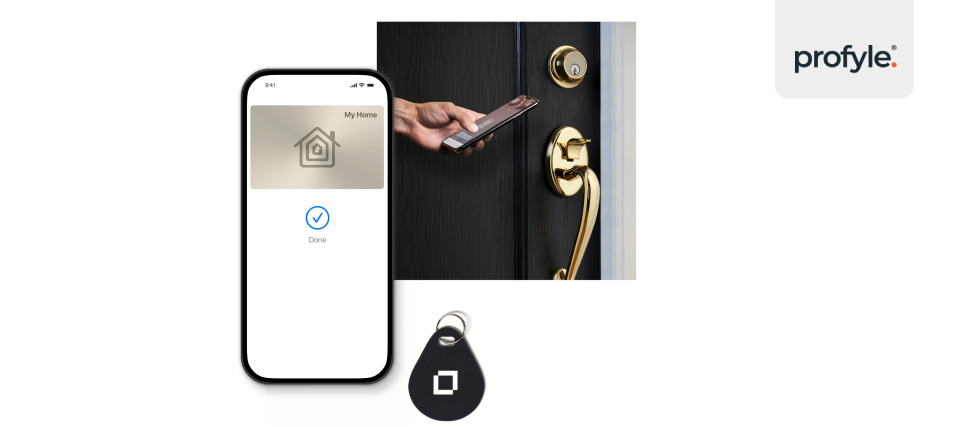
NFC tags are also used for security and access control in many offices and homes. Instead of carrying a traditional key or even a key card, people can now use NFC-enabled badges or phones to unlock doors with a simple tap. This not only adds convenience but also enhances security by reducing the risk of lost or stolen keys.
Some events now use badges with NFC tags. Attendees can tap booths to register their interest or collect product info, just by tapping their badges.

One of the more exciting uses for NFC tags in the professional world is digital business cards. Companies like Profyle have embraced this technology to make networking easier. With a Profyle Digital Business Card, all you need to do is tap your phone against someone else’s phone. Then your contact information is instantly shared with them. There is no need for paper cards that often get lost or thrown away. Your details are stored digitally. This makes it easy to share and track professional connections.
NFC tags are also used in marketing. You may have seen posters that prompt you to tap your phone for more information or special offers. These smart posters contain NFC tags that link you to websites, videos, or promotional deals when you tap your phone. It’s a seamless way for businesses to engage customers without requiring them to type in web addresses or scan QR codes.

Another great use of NFC tags is on product packaging. Some companies include NFC tags on their products. Consumers can tap their phones to get more info, like ingredients, instructions, or where it was made.
NFC tags help businesses share information faster and make their daily operations smoother. Here’s why they are becoming so popular:
NFC tags are making it easier to interact with the world. They let us pay for coffee with a tap of our phones. They also let us share our details with digital business cards like Profyle.

Profyle has taken the potential of NFC technology and used it to make networking more seamless. With Profyle Digital Business Cards, you don’t need to worry about carrying around stacks of paper cards. You can store all your contact details digitally and share them with just a tap.
In order to use NFC tags, you need a NFC tag reader. An NFC tag reader is a feature in many devices, like smartphones, tablets, and payment terminals. It lets them interact with NFC tags. The reader’s job is to detect and receive information stored on the NFC tag when the device gets close enough to it—usually within a few centimetres.
Think of the NFC tag as a “sticker” with information on it, and the NFC reader is like a scanner that picks up that information. When these two come close to each other, the NFC reader picks up the signal from the tag, allowing the device to access the data stored on it. This could be anything from a website link to contact information or even a command to open an app.
NFC readers can be found in:
The technology behind NFC tag readers is fascinating, but it operates in a straightforward way. Let’s break down how it works step by step.
Sign up for our free 45-day trial and experience the future of networking today. Embrace efficiency, embrace sustainability, embrace the future with Profyle Card.
Don’t forget to follow us on LinkedIn, Instagram and Twitter
Copyright © 2025 Profyle Card Ltd. – Registered in England and Wales with company number 12973729.
Business address: 16 Cole Street, London, SE1 4YH, United Kingdom. VAT registration number: GB424998061