
QR technology, often referred to simply as QR, stands for Quick Response technology. QR codes are a type of barcode. They can store a lot of data. You can quickly access it by scanning the code with a smartphone or similar device.
Traditional barcodes store info in a one-dimensional (1D) format (lines of varying widths). QR codes use two dimensions (2D), so they can store much more data.

Over the past few years, QR codes have become a major part of everyday life. Did you know that the use of QR codes surged by 94% from 2019 to 2021? The COVID-19 pandemic in particular drove this because of health and safety reasons.
QR codes still remain popular. You might have seen them on product packaging, flyers, ads, and restaurant menus. But how do they function, what are their purposes, and are they secure?
As mentioned, QR stands for Quick Response. This name reflects QR codes’ main purpose: to quickly and easily access information. You don’t need to type a web address or search for a product. Just scan the code, and the info goes to your device. This speed and convenience are what has made these codes so popular in a wide variety of industries.
That is appreciated by consumers and end-users worldwide. For example, the US leads the world in QR scans. There in 2023, 91 million smartphone users scanned QR codes.
QR codes work by encoding information in a pattern of black and white squares. The black squares represent data, while the white spaces are there to help the scanner read the code.
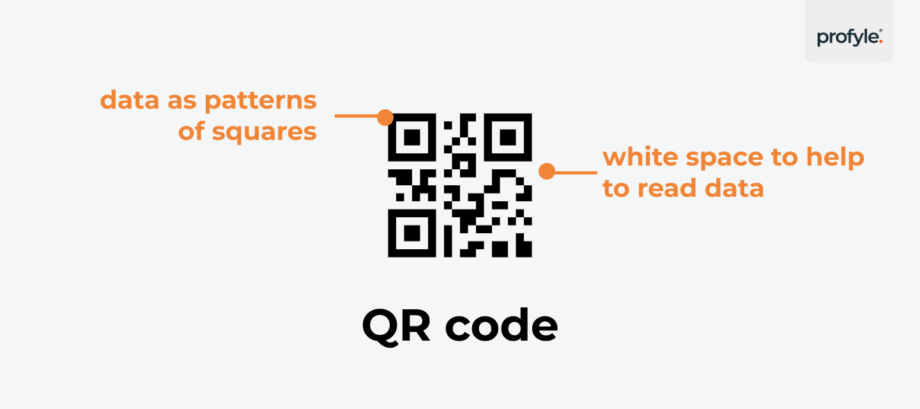
When you scan a QR code with your device, its camera reads it. It interprets the pattern of squares as data. This data can be anything from a web address (URL) to a contact card, a payment request, or even a simple piece of text.
Most modern smartphones have built-in QR code readers. So, you don’t need to download an app to scan a code. Just open your camera app. Point it at the code. Your phone will recognize it and display a link to the encoded information.
That’s very convenient. It has led to mass adoption of QR payments, especially in Asia. Consumers can pay by scanning a QR code at restaurants, street vendors, or small businesses.

QR codes were invented in 1994 by Masahiro Hara, an engineer working for Denso Wave, a subsidiary of Toyota. They were created for tracking parts in the automotive industry’s manufacturing process. Traditional barcodes, commonly used at the time, were too limited in their ability to store information. QR codes were designed to store more data and allow for quicker scanning.
The original goal was to create a system that could hold more data while being easier to scan, hence the name “Quick Response.” Therefore, QR codes were initially meant for factories. Their potential soon became clear in other fields. So, their use quickly spread beyond manufacturing.

Today, QR codes are used in many different ways. Some of the most common uses of QR technology include:
Marketing and Advertising: QR codes are often used in marketing campaigns. Companies print them on flyers, posters, and product packaging. They do this to direct consumers to websites, promotions, or special offers. For example, a poster advertising a new film might include a QR code that leads to the film’s trailer. Interestingly, 62% of QR scans are done by people aged 25-34 – an attractive demographic for advertisers.
Payments: QR codes have become a popular way to make payments. Apps like PayPal, Venmo, and others allow users to scan a code to send or receive money. This can be much faster and easier than entering account details manually.
Product Information: QR codes on product packaging can provide extra info. This includes nutritional details for food, usage instructions, and customer reviews.
Contactless Menus: Since COVID-19, many restaurants use QR codes for digital menus. Diners can scan the code with their phones to view the menu. This reduces contact between customers since they won’t touch a physical menu.
Wi-Fi Access: In some places, QR codes are used to share Wi-Fi credentials. Instead of typing a long, complex password, scan the QR code. Your phone will then connect to the network.
Event Tickets: Many event organisers now use QR codes as digital tickets. When you buy a ticket online, you might receive a QR code, which you can show at the entrance to the event. The code is scanned, and your ticket is validated instantly.
Medical Info: In healthcare, QR codes store important medical info. Some people carry QR codes on cards or bracelets. These codes link to their medical history or allergy info for emergencies. The medical field is the one that Masahiro Hara, the creator of QR codes, sees as the most promising for the technology.
The technology behind QR codes is quite fascinating. Old-school barcodes are limited to a single line of data. Unlike traditional barcodes, QR codes use a matrix of black and white squares. This matrix lets them store info both vertically and horizontally. It greatly increases their data capacity.
QR codes can store up to 7,000 digits or 4,000 characters of text, depending on the version of the code being used. They also have error correction. So, they can work even if some code is damaged or obscured. This is why you can often still scan a QR code even if it’s slightly crumpled or dirty.
When you scan a QR code, your device’s camera reads the pattern. It then converts it into readable data. If the QR code contains a URL, your phone’s browser will open that webpage. If it contains text, the text will be displayed. If it contains an action, such as making a payment, your phone will guide you through the process.

When you scan a QR code, your phone reads the pattern of black and white squares. It then decodes them into a string of information. This info might be a URL, text, or a command. It may prompt you to pay or save a contact.
Here’s what typically happens in the background:
Image Capture: The scanner captures an image of the QR code.
Pattern Recognition: The software recognises the black and white pattern as a QR code.
Decoding: The QR code is decoded, and the information it holds is extracted.
Action: The device takes action based on the type of data in the QR code. For example, it might open a webpage, show you text, or prompt you to complete a transaction.
For the most part, QR codes are safe to use. However, like any technology, they can be misused by people with bad intentions. A QR code could link to a fake website. It could steal your personal info or download malware to your phone.
Here are some risks associated with QR codes:
Phishing: A malicious QR code could take you to a fake, but real-looking, website. It’s designed to steal your data, like your login and credit card info.
Malware: A malicious QR code could direct your phone to download malware, which could harm your device or steal information.
Fraudulent Payments: Some scammers create fake QR codes for payments. They trick people into sending money to the wrong place.
To stay safe when using QR codes, follow these simple guidelines:
Only scan codes from trusted sources.
Double-check the URL before clicking on any links.
Avoid scanning codes in unfamiliar places or from suspicious-looking materials.
Technically, a QR code itself doesn’t expire, but the information it links to can become outdated or unavailable. For example, if a QR code links to a website, and that website is taken down, the QR code will no longer function. Similarly, if a QR code links to a time-sensitive event or promotion, it will no longer be relevant once the event is over.
Some QR codes are dynamic, meaning that the data linked to the code can be updated even after the code has been printed. This allows businesses to change the information that the QR code points to without having to print new codes. For example, a restaurant might use the same QR code to update its menu daily.

While QR codes have many advantages, they also have some downsides. Here are a few disadvantages:
Security Risks: As mentioned earlier, QR codes can be misused for phishing or to spread malware.
Technology Dependence: Some people lack smartphones with cameras and internet. This limits QR code use in some areas and among certain groups.
User Hesitance: Some are hesitant to use QR codes. They are unfamiliar with the technology, don’t know how to scan the codes, or are concerned about privacy and security.
Temporary Relevance: QR codes that link to time-sensitive content, like an event or promotion, can become obsolete once that event or promotion is over.
While QR codes are still widely used today, there are emerging technologies that could potentially replace them in the future. Some of these include:
NFC (Near Field Communication): NFC allows two devices to communicate when they are close to each other. Many smartphones already have NFC capabilities, and it’s commonly used for contactless payments. Unlike QR codes, NFC doesn’t require the user to scan anything; they simply hold their phone near the NFC tag, and the action is triggered.
Augmented Reality (AR): Augmented reality technology allows users to interact with the physical world in new ways. In the future, AR could replace QR codes. Users could point their phones at an object or image. They would then get digital info instantly, like with a QR code today.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): BLE technology is another possible replacement for QR codes. BLE beacons can send info to nearby devices. Users can then receive messages or promotions without scanning a code.
As with any technology, QR codes come with some risks. The main risks associated with QR codes include:
Phishing: Scammers can create QR codes that link to fake websites designed to steal personal information.
Malware: Some malicious QR codes can direct users to download malware onto their devices.
Fake Payment Links: Fraudsters might use QR codes to trick people into making payments to the wrong account.
To protect yourself, always scan QR codes from trusted sources. Be cautious with codes from unfamiliar locations.
QR codes are simple and their versatility makes them popular. So they will likely remain a key tool for years. But new tech like NFC, AR, and BLE may replace QR codes. That’s because they may offer better ways to interact with digital content.
In the meantime, QR codes are a quick, easy way to share info. Just scan with your phone for instant access.
Sign up for our free 45-day trial and experience the future of networking today. Embrace efficiency, embrace sustainability, embrace the future with Profyle Card.
Don’t forget to follow us on LinkedIn, Instagram and Twitter
Copyright © 2025 Profyle Card Ltd. – Registered in England and Wales with company number 12973729.
Business address: 16 Cole Street, London, SE1 4YH, United Kingdom. VAT registration number: GB424998061